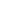
Statistical Analysis of the Bureau of Meteorology's Evaporation Datasets
Ryan Watson Consulting was contracted to conduct statistical analysis of the Bureau of Meteorology’s (BoM) automated and manual evaporation datasets, with the aim of demonstrating that automated weather recording stations produce reliable data.
Analysis of data for both manual and automated systems was performed using several methods for selected stations around Australia (see figure). Exploratory analysis was carried out using R within R Studio and Excel. However, for the final analysis, Jupyter Notebooks were employed since this provided the capability to do extensive analysis programmatically.
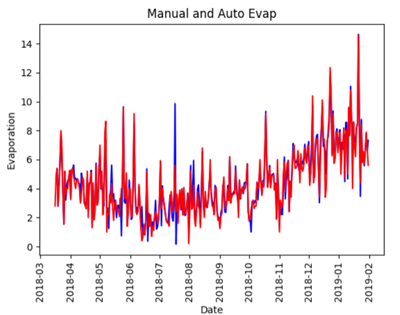
The results showed that the manual/automated evaporation ratio was close to 1.0 for most stations providing confidence in the application of automated collecting stations (refer to figure). Further correlation analysis was performed for one station to study how the difference between manual and automated systems was affected by other weather conditions such as rain, wind, humidity and solar radiation. However these conditions had little effect on the ratio of automated to manual evaporation.
All the materials developed by our company including a detailed report were provided to the BoM.